4 Types of Gear Failure to Watch Out For
- Share
- publisher
- pairgears
- Issue Time
- Feb 23,2025
Summary
Learn the four most common gear failures — wear, pitting, fracture, backlash — and how preventive design and maintenance ensure gear reliability.

1. Introduction
At PairGears, we know that gears are the backbone of modern machinery — from agricultural tractors and heavy-duty trucks to industrial automation and robotics. While high-quality gears are engineered for strength and longevity, even the most durable systems are not immune to failure.
Gear failure analysis helps manufacturers and operators understand why gears fail, what conditions trigger these issues, and how to prevent them through better design, materials, and maintenance.
This article examines four of the most common gear failures that every engineer and operator should monitor, along with practical prevention strategies.
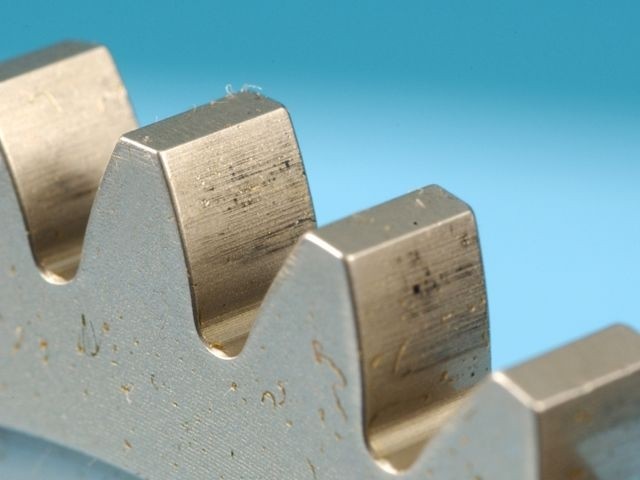

2. Gear Tooth Wear
2.1 What It Is
Gear tooth wear is the gradual loss of material from gear teeth due to frictional contact during operation. Left unchecked, it reduces contact accuracy and may cause slippage.
2.2 Causes
• Poor lubrication → metal-to-metal contact accelerates wear.
• Misalignment → uneven load distribution damages tooth flanks.
• Overloading → excessive torque accelerates material loss.
2.3 Prevention
• Apply high-quality gear lubricants suitable for your application (See gear lubrication methods).
• Regularly check alignment during installation and maintenance.
• Use load monitoring to prevent exceeding design torque.
Explore our Precision Gear Manufacturing.
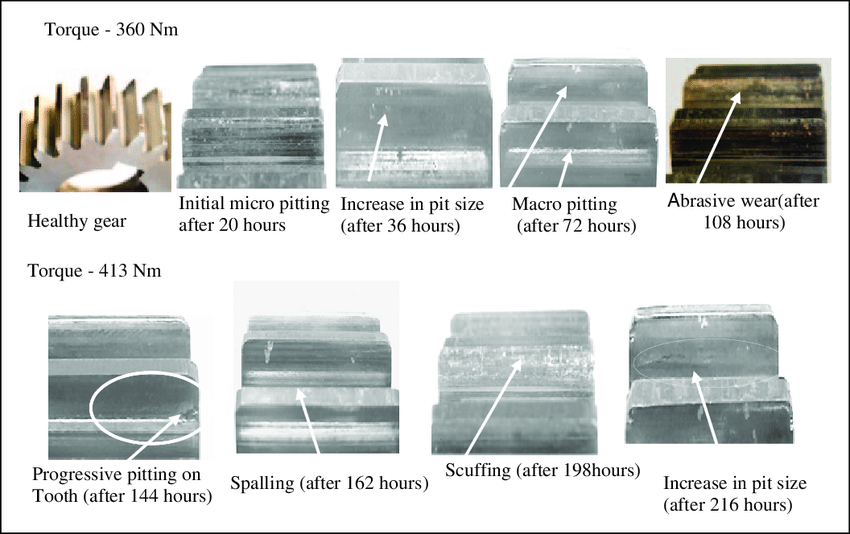
3. Pitting and Scuffing
3.1 What They Are
• Pitting → fatigue-induced cavities on tooth surfaces.
• Scuffing → severe tearing of material due to excessive friction and heat.
3.2 Causes
• High operational loads and elevated temperatures.
• Inadequate lubrication film under extreme pressure.
3.3 Prevention
• Use lubricants with high-pressure and high-temperature resistance.
• Avoid overload conditions by adhering to manufacturer’s specs.
• Conduct scheduled inspections to replace worn gears early

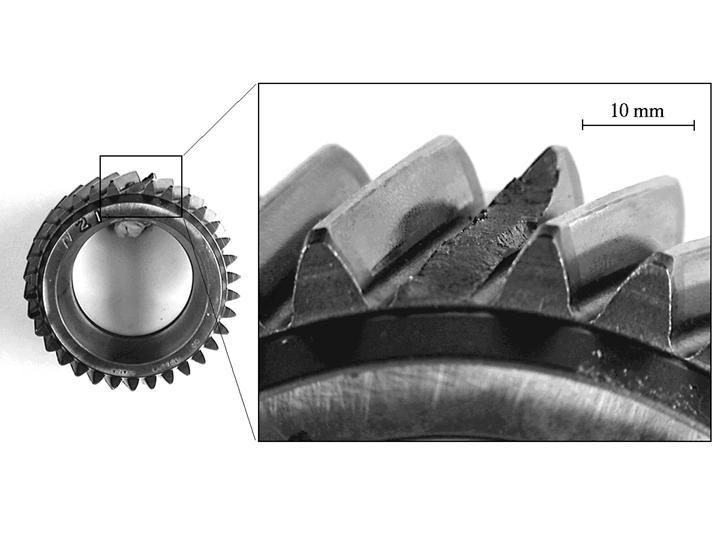
4. Tooth Fracture
4.1 What It Is
Tooth fracture occurs when one or more gear teeth crack or break off completely. This type of failure can cause system shutdowns and secondary damage to connected components.
4.2 Causes
• Overloading → torque levels beyond design limit.
• Fatigue stress → micro-cracks accumulate in high-cycle operations.
4.3 Prevention
• Operate gears within specified load limits.
• Select high-strength alloys and surface treatments such as carburizing or induction hardening.
• Employ advanced finite element analysis (FEA) during design to predict stress points.
Learn about our Custom Gear Design Solutions.
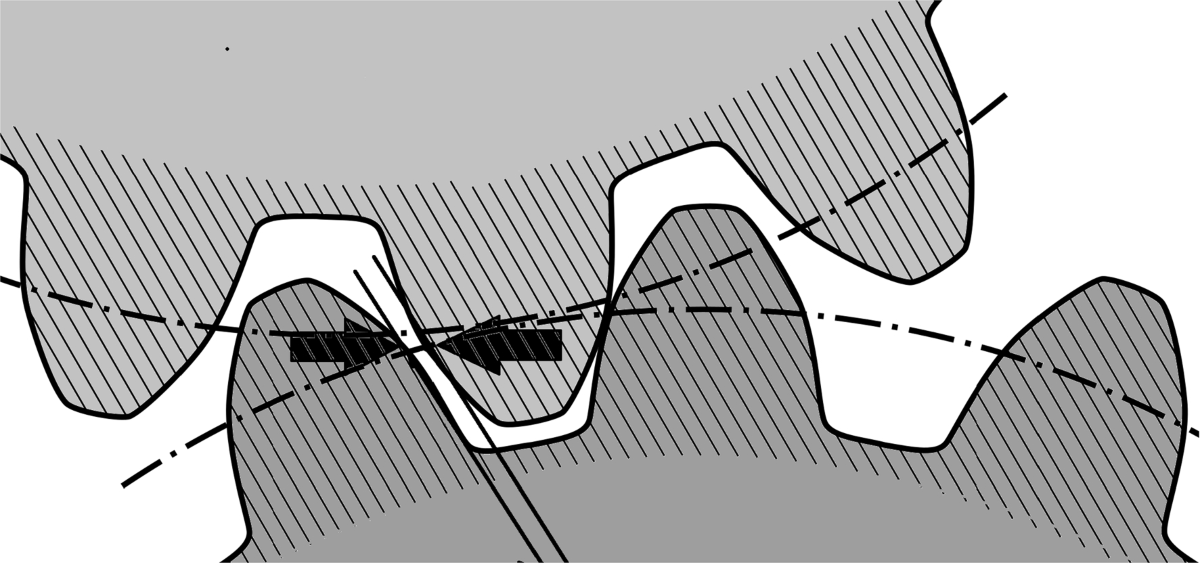
5. Gear Backlash
5.1 What It Is
Backlash is the clearance or play between mating gear teeth when reversing motion. While some backlash is necessary, excessive backlash leads to inaccuracies and accelerated wear.
5.2 Causes
• Incorrect installation → improper meshing during setup.
• Progressive wear → loss of tooth material increases spacing.
5.3 Prevention
• Maintain correct tooth clearance during assembly.
• Inspect for looseness or unusual gear play during routine checks.
• Use precision gears designed with tight tolerances to minimize backlash.
6. Preventing Gear Failures: Best Practices
6.1 Choose the Right Materials
Selecting the right alloy is critical. Case-hardened steels, alloy steels, or bronze gears can provide superior wear resistance and fatigue life.
6.2 Proper Maintenance
Implementing a preventive maintenance program ensures issues are detected early. Inspections should include lubrication checks, alignment verification, and vibration monitoring.
6.3 Load Management
Ensure gear systems operate within specified design limits. Modern sensors can track loads and temperatures in real time, preventing catastrophic failure.
External reference: AGMA Gear Standards.
Conclusion
Gear failures — whether tooth wear, pitting, fractures, or backlash — can cause costly downtime and equipment damage. By applying rigorous gear failure analysis, following preventive measures, and selecting the right gear manufacturer, companies can extend the lifespan of their machinery and maintain reliable performance.
At PairGears, we engineer gears with precision craftsmanship, advanced heat treatments, and strict quality control to reduce the risk of failure. Whether you need OEM gear design, custom gear solutions, or gear replacement, our team ensures reliability and efficiency.
📩 Should you have any questions or require further assistance, please do not hesitate to contact our engineer: ben@pairgears.com.







