Choosing the Right Material for Gears: An Overview
- Share
- publisher
- pairgears
- Issue Time
- Jul 24,2024
Summary
Selecting the right gear material is key. This article reviews copper, iron, aluminum alloys, tool steel, and thermoplastics, highlighting their unique benefits and uses.

Introduction
When designing an individual gear or a gear train, the choice of material will either be the primary factor on which the gear geometry is based or the gear performance will dictate the proper material selection. There are various raw materials that are commonly used in gear construction, and each one has a sweet spot where its mechanical properties stand out as the superior choice. The main categories of materials are copper alloys, iron alloys, aluminum alloys, and thermoplastics.
Copper Alloys
Copper alloys are ideal for gears exposed to corrosive environments or requiring non-magnetic properties. Common types include:
1.Brass: An alloy of copper and zinc, brass is easy to machine and offers antimicrobial benefits. It’s often used in spur gears and gear racks in low-load environments.
2.Phosphor Bronze: Combining copper with tin and phosphorus, this alloy provides excellent wear and corrosion resistance. It’s used in high-friction components like worm wheels.
3.Aluminum Bronze: With copper, aluminum, iron, nickel, and manganese, this alloy offers superior wear and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for high-load gears like crossed-axis helical gears and worm wheels.

Iron Alloys

Iron alloys, known for their superior strength, include:
1.Gray Iron: Cast and machined into gears, gray iron is a good alternative to phosphor bronze where magnetic fields are not a concern.
2.Carbon Steel: Widely used for its machinability, wear resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Carbon steels vary in carbon content and can be hardened or case-hardened to increase strength and load capacity.
3.Alloy Steel: Contains additional elements like chromium and nickel, offering enhanced strength, machinability, and corrosion resistance. Commonly used for high-strength gears.
4.Stainless Steel: Contains chromium and other trace elements, offering excellent corrosion resistance. 303 and 316 alloys are commonly used for spur gears, helical gears, and bevel gears.
Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloys are known for their high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. Common types include:
1.2024 Aluminum: High strength but lower corrosion resistance.
2.6061 Aluminum: Medium strength with good corrosion resistance and weldability.
3.7075 Aluminum: High strength and stress resistance.
These alloys are used for spur gears, helical gears, straight tooth bevel gears, and gear racks, though they are less suitable for high-heat environments.

Tool Steel Alloys
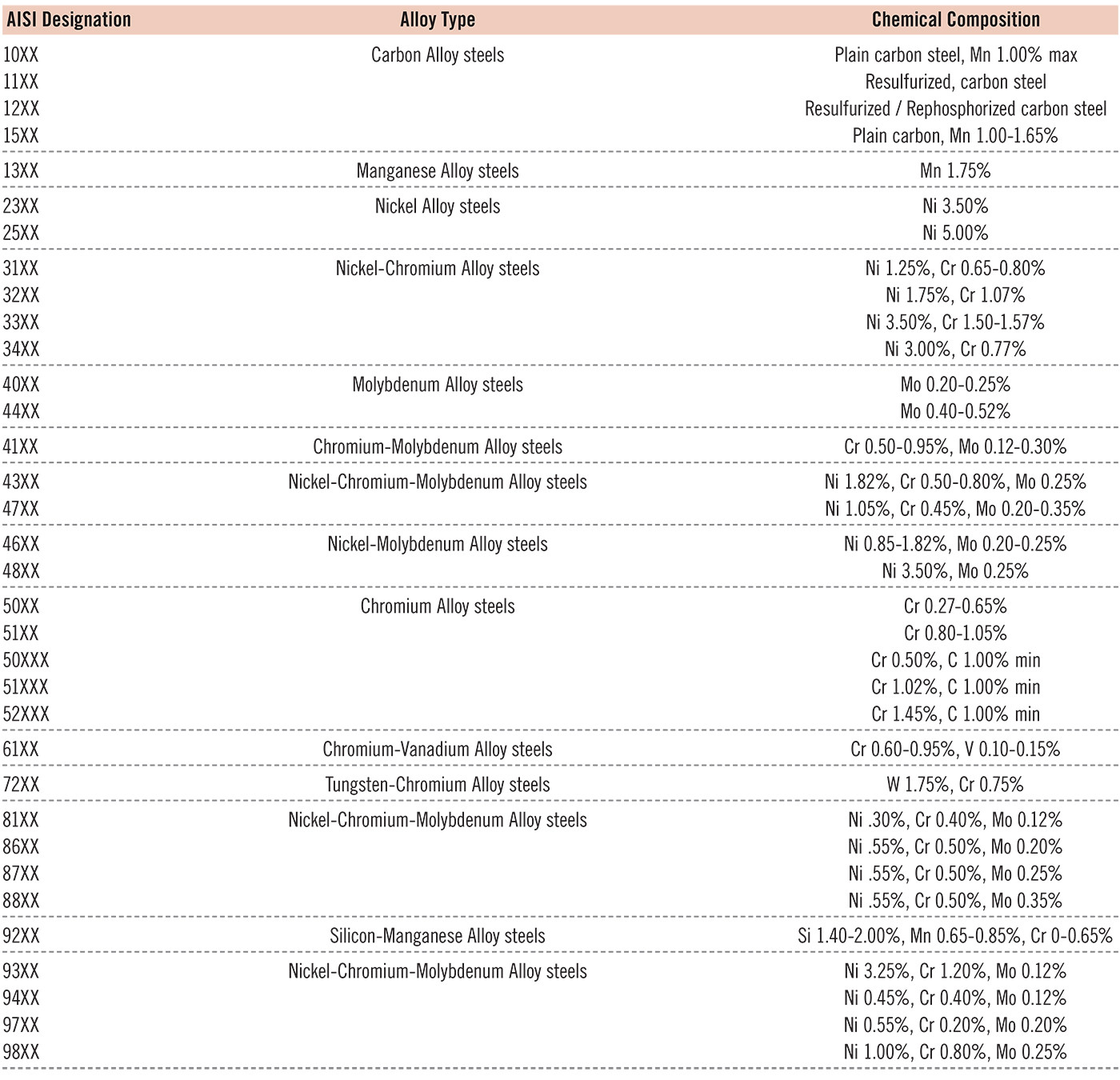
The fourth group of alloys is tool steels. These are steel alloys with traces of cobalt, molybdenum, tungsten, and/or vanadium. These elements add heat resistance and durability to the steel.
AISI identifies steel alloys using a four-digit sequence. The first two digits designate the alloy family, and the last two digits designate the fractional percentage of carbon. For example, a 1020 carbon steel has a 0.20% carbon content, whereas a 1045 carbon steel has a 0.45% carbon content.
Thermoplastics
Thermoplastics are chosen for their lightweight and machinability. Common materials include:
1.Acetal (POM): Known for dimensional stability and low friction. It’s ideal for wear surfaces but less suitable for shock loading applications.
2.Nylon: Offers high strength and vibration absorption but may become unstable with moisture and temperature changes. It can be reinforced with fibers for increased strength.
The Future: Unobtainium

While not yet developed, unobtainium represents the ideal gear material, combining extreme lightness, hardness, low friction, and cost-effectiveness. When invented, it will revolutionize gear manufacturing.
Conclusion
In summary, selecting the right material for gear manufacturing is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Copper alloys, iron alloys, aluminum alloys, tool steels, and thermoplastics each offer distinct advantages that cater to specific operational requirements. By understanding the unique properties of these materials, engineers can make informed decisions that enhance gear performance and reliability.
At PairGears, we leverage our extensive knowledge and experience in gear manufacturing to provide high-quality gears tailored to meet diverse industry needs. Our commitment to using the best materials and advanced manufacturing techniques ensures that our gears deliver superior performance, durability, and efficiency. Trust PairGears for all your gear manufacturing needs, where precision and excellence are our top priorities.
Should you have any questions or require further assistance, please do not hesitate to contact our engineer ben@pairgears.com.