Choosing the Right Gear Manufacturing Process: Hobbing, Shaping and Grinding
- Share
- publisher
- pairgears
- Issue Time
- Aug 8,2024
Summary
Manufacturing methods for gears mainly include gear hobbing, gear shaping, and gear grinding, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages.

Introduction
When it comes to manufacturing gears, selecting the appropriate process is crucial for ensuring both efficiency and quality. In this article, we will delve into three primary gear manufacturing methods: hobbing, shaping and grinding, providing a detailed analysis of each.

Hobbing: A Fast and Efficient Method
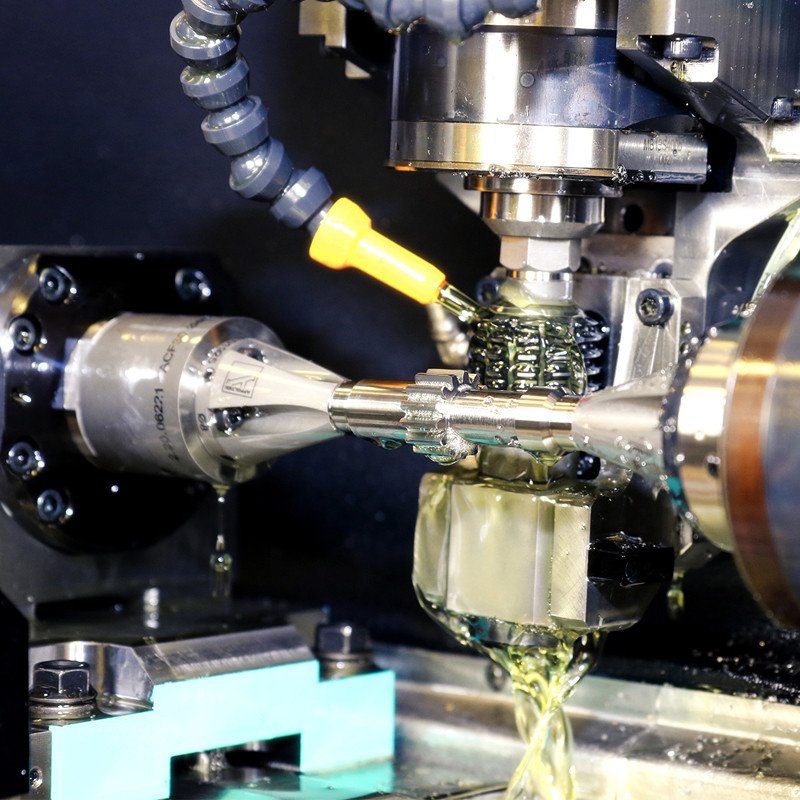
Advantages of Hobbing:
1. Speed: Hobbing is known for its rapid production capabilities, making it ideal for high-volume runs.
2. Versatility: It can be used to manufacture various gear types, including spur, helical, and worm gears.
3. Precision: Modern hobbing machines are capable of achieving high levels of accuracy in gear tooth profiles.
Disadvantages of Hobbing:
1. Material Limitations: Hobbing can be less effective for very hard or brittle materials.
2. Surface Finish: The surface finish may require additional processes to meet certain standards.
Shaping: A Traditional Yet Reliable Option
Advantages of Shaping:
1. Good Surface Finish: Shaping often results in a better surface finish than hobbing.
2. Hard Materials: It can effectively work with harder materials that may not be suitable for hobbing.
Disadvantages of Shaping:
1. Speed Limitations: Shaping is generally slower, making it less suitable for high-volume production.
2. Tool Wear: The cutting tools can wear out more quickly due to the nature of the process.
Grinding: Precision at Its Finest
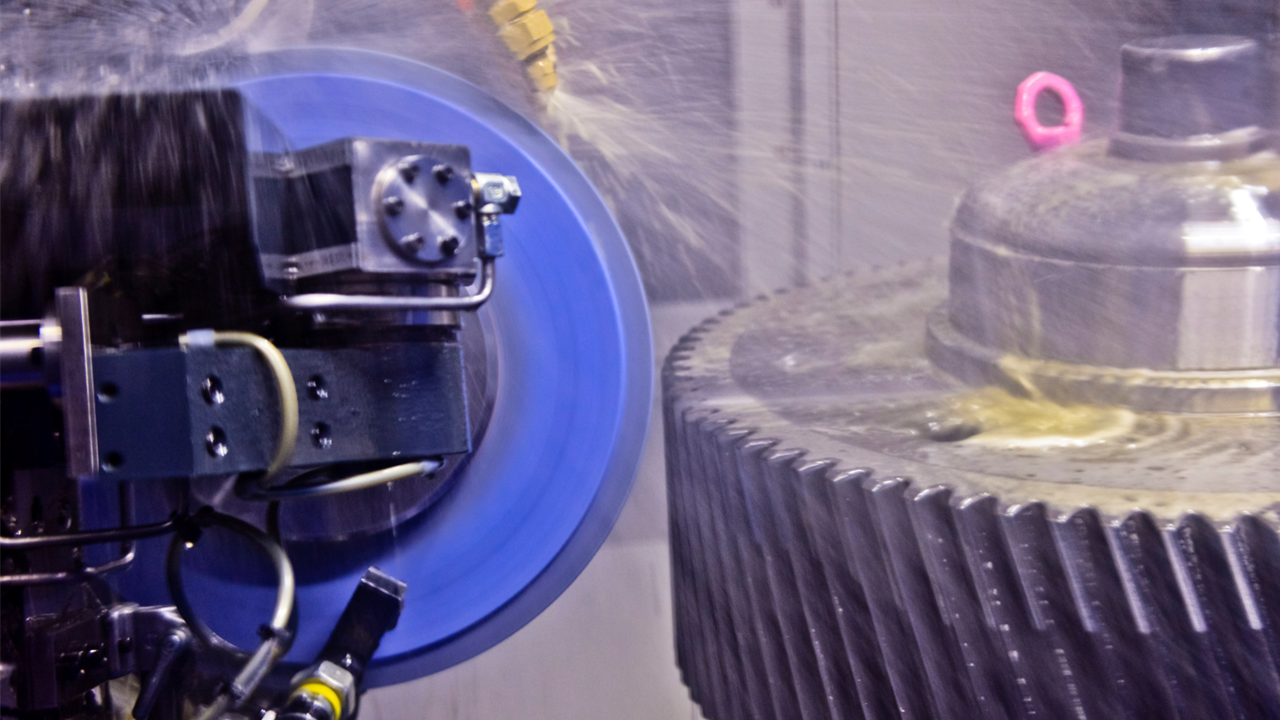

Advantages of Grinding:
1. High Precision: Grinding offers exceptional accuracy and is ideal for gears that require tight tolerances.
2. Excellent Surface Finish: The process achieves a highly polished surface, which can enhance gear performance.
Disadvantages of Grinding:
1. High cost: Gear grinding machines are expensive, and the grinding process itself is time-consuming and consumes materials, leading to higher production costs.
2. Lower efficiency: Gear grinding has a slower processing speed and is not suitable for mass production.
Conclusion
Choosing the right gear manufacturing process—be it hobbing, shaping, or grinding—depends on various factors including production volume, material type, and precision requirements. Hobbing is excellent for large-scale production, shaping is reliable for producing quality shapes, and grinding excels in precision applications. By carefully considering each method's advantages and disadvantages, manufacturers can ensure they select the best approach for their specific needs.
Our YouTube channel will be updated frequently with our gear production process videos, if you are interested, you can click the link below to follow our channel, there are wonderful videos every week!
↓ ↓ ↓
Should you have any questions or require further assistance, please do not hesitate to contact our engineer: ben@pairgears.com.